Seleucia Pieria
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Seleucia in Pieria (Greek Σελεύκεια ἐν Πιερίᾳ), also known in English as Seleucia by the Sea, and later named Suedia, was a Hellenistic town, the seaport of Antioch ad Orontes (Syria Prima), the Seleucid capital, modern Antakya (Turkey). The city was built slightly to the north of the estuary of the river Orontes, between small rivers on the western slopes of the Coryphaeus, one of the southern summits of the Amanus Mountains.
According to Pausanias and Malalas, there was a previous city here named Palaeopolis ("Old City"). At present, it is located at the seaside village of Çevlik[1]
near the town of Samandağ in the Hatay Province of Turkey. Seleucia, Apamea, Laodicea, and Antioch formed the Syrian tetrapolis.[2]
History
Seleucid period
Seleucia Pieria was founded in ca. 300 BC by Seleucus I Nicator, one of the successors of the Macedonian conqueror Alexander the Great and the founder of the Seleucid Empire.[3]
The Macedonians called the landscape Pieria, after a district in their
homeland that was also between the sea and a mountain range (the
Olympus).[3]
When Seleucus I was murdered on his way to Macedon in 281 BC, his
son, Antiochus I, buried his ashes in a building called "Nikatoreion",
situated on Seleucia.
The city was of great importance in the struggle between the Seleucids and the Ptolemies; it was captured by Ptolemy Euergetes in 246 BC.[2] As the Ptolemies (Lagids) and Seleucids fought over the city, it changed hands several times until 219 BC, when the Seleucid Antiochus III the Great recaptured it during the Fourth Syrian War (219–217 BC) his general Ardys is recorded as having distinguished himself during the siege. Then it obtained its freedom and kept it even to the end of the Roman occupation. It had long enjoyed the right of coinage.[4]
Roman period
When the Seleucid Empire was subdued by the Armenian conqueror Tigranes II, Seleucia Pieria resisted. Roman general Pompey the Great restored the Seleucids to power by giving the city to Antiochus I Theos of Commagene, a direct descendant of Seleucus I Nicator and a loyal ally of Rome. Under light Commagene rule, Seleucia enjoyed substantial autonomy, i.e. de facto independence.[3]
Seleucia's importance grew significantly over time, necessitating the enlargement of its harbours several times under Diocletian and Constantius. These harbours, called the "inner" and "outer" harbours, served from time to time the Roman navy.
Most buildings and structures today date from the Roman period.
Byzantine period
During Byzantine
times the city went into a steady decline. The silting up of the city's
harbours hastened this process. In the fifth century CE the fight to
keep them open was finally given up. It suffered severely in the
devastating 526 Antioch earthquake.
Islamic period
Seleucia was captured by the Sasanids around 540 CE. While it never recovered as a port-city again, Al-Walid ibn Abd al-Malik, Ummayad Caliph from 705 to 715, built a fortress in the city.[5]
Seleucia Pieria and Christianity
The city was Christianized early. As the port of Antioch of Syria,[2]
"Seleucia on sea"—so called to distinguish it from other cities of the
same name—is most notable as the precise point of embarkation from which
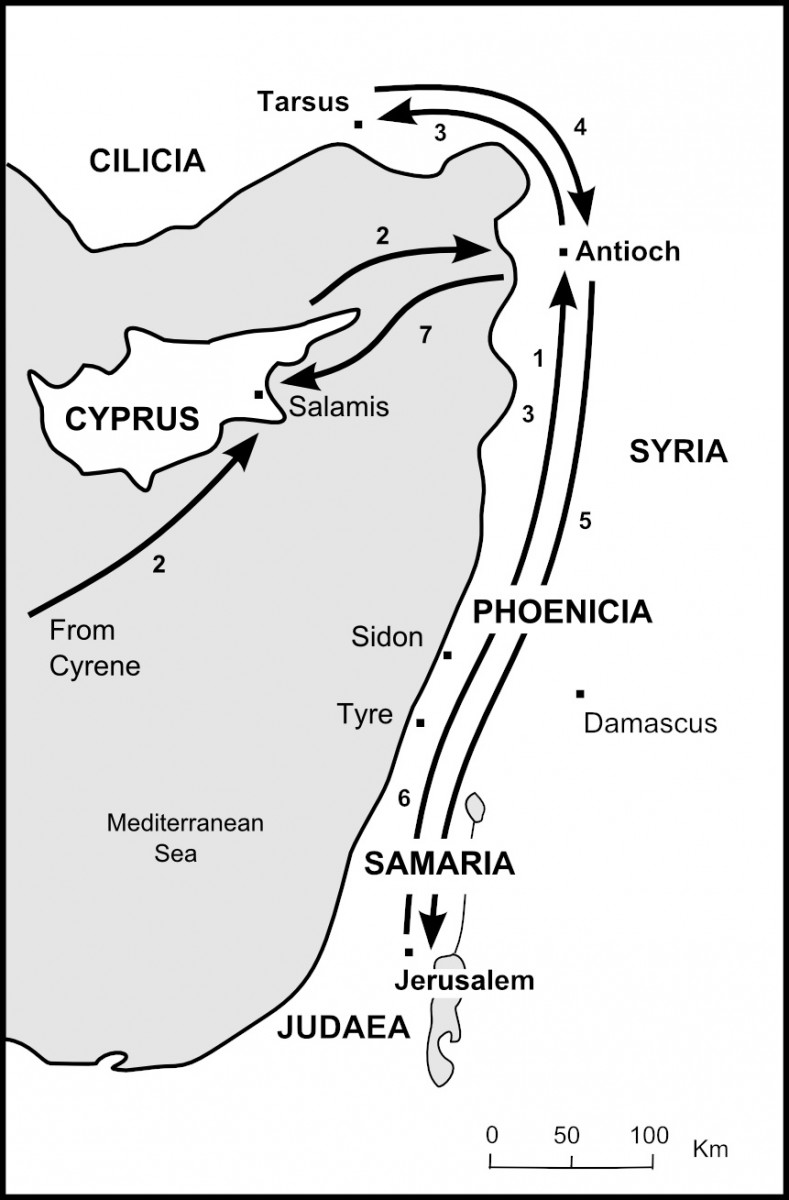
the Apostle Paul [in 45 CE] and Saint Barnabas sailed from this port on their first missionary journeys, as chronicled in the Bible (Acts 13:4).[6]
At the end of that same journey he must have made landfall at Seleucia
before going to Antioch (see Acts 14:26). His route at the beginning of
the second journey was by land and probably bypassed Seleucia (see Acts
15:40–41), though on returning, he must have passed through it again
(see Acts 18:22). Once more taking a land route when setting out on his
third journey, Paul may have missed Seleucia (see Acts 19:1), and at
that journey's end he did not return to Antioch and so missed Seleucia
again (see Acts 21:7–8). This means that Paul passed through Seleucia at
least three times, and probably several more on pre-missionary visits
to Antioch of Syria (see Acts 11:26; 12:25).
The oldest bishop known is Zenobius, present at the Council of Nicaea in 325 CE. Other known bishops include Eusebius, an Arian, and Bizus in the fourth century, with twelve others cited by Le Quien (Oriens Christianus, II, 777–780). In the sixth century CE the Notitia Episcopatuum of Antioch, gives Seleucia Pieria as an autocephalous archbishopric, suffragan of Antioch (Échos d'Orient, X 144); the diocese existed until the tenth century CE, and its boundaries are known (Échos d'Orient, X, 97). For some Roman Catholic titularies see Eubel, Hierarchia catholica medii aevi, I, 468.[4]
Seleucia Pieria was a diocese of the Syriac Orthodox Church
in the eighth and ninth centuries CE, three of whose bishops are known.
The last-known Syriac Orthodox bishop of Seleucia, Ahron (847/874 CE),
is mentioned in the lists of Michael the Syrian. There were also Georgian monastic establishments around Seleucia from the 11th to the 13th centuries.[7]
The city is still a titular see of the Roman Catholic Church, Seleuciensis Pierius; the seat is vacant following the death of the last bishop in 1980.[8]
A section of the
Titus Tunnel
Known bishops
- Eugenius of Seleucia heretical follower of Athanasius, grandson of Empress Theodora[9]
- Dositheus I[10]
- Zenobius, present at the Council of Nicaea in 325 CE.
- Eusebius 350[10]
- Bizus fl 381
- Maximus
- Vasilius of Seleucia, Attendee of Council of Ephesus in 431,[11] supporter of Nestorius.
- Basil of Seleucia fl 452.
- Dositheus II fl 553.
- Gerontius fl 448.
- Nonus of Seleucia; from about 505 AD, exiled about 521 for heresy.
- Constantius, a heretic
- Dyonisis fl 553
- Antonius,[10]
- Theodorus
- Agapoius
- Nicholas
- Ahron (847–874 CE).[12]
Greek rite bishops
Latin titular archbishop
Main sites
The
upper city, about 13 km in circumference, is still distinguishable. The
lower city, smaller than the preceding one, was more thickly populated.[4] Ruins include a necropolis, amphitheatre, citadel, temples, some irrigation works as well as some fortifications.
The highlight of the city is a 1350–1400m-long tunnel/canal complex built during Roman
times. It is believed that it was dug to divert the nearby river and
prevent the harbour from silting up with time. A further reason is
assumed to be to help reduce flooding caused during heavy winter rains.
Construction began during the reign of Emperor Vespasian (69–79 CE) continuing mainly during his son Titus's time (79–81 CE).
According to Flavius Josephus, a Roman-Jewish historian (37–ca.100 CE), Jewish slaves were used as workers. These were working under orders of Emperor Titus, who had captured Jerusalem in 70 CE. Other POWs were sent to Rome, where they had to build the Colosseum. According to an inscription, the tunnel/canal was not completely finished until the reign of Antoninus Pius (138–161 CE). The last workers were Roman legionaries.[3]
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sergius_Paulus
Sergius Paulus
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Lucius Sergius Paulus or Paullus was a Proconsul of Cyprus under Claudius (1st century AD). He appears in Acts 13:6-12, where in Paphos, Paul, accompanied by Barnabas and John Mark, overcame the attempts of Bar-Jesus (Elymas) "to turn the proconsul away from the faith" and converted Sergius to Christianity.
A boundary stone of Claudius mentioning Sergius was discovered at Rome in 1887.[1] It records the appointment (AD 47) of the Curators of the banks and the channel of the river Tiber,
one of whom was Sergius. Since Paul's journey to Cyprus is usually
dated to the first half of the 40s (and some scholars date his visit
even earlier), it is thought Sergius may have first served three years
as Proconsul at Cyprus, then returned to Rome, where he was appointed curator.[2] Another inscription was discovered in 1887 at Soli, Cyprus, by Luigi Palma di Cesnola which mentions a proconsul Paulus.[3] This inscription was dated to the middle of the first century by D.G. Hogarth.[4]
T.B. Mitford noted that based on epigraphic grounds the inscription
cannot be dated earlier than this and is probably considerably later.[5] As he is not greeted in Paul's Epistle to the Romans, it is possible he died before it was written.[6]
Some medieval legends have anachronistically identified Sergius Paulus with Paul of Narbonne.
Sergius Paulus may have been the first of several successive senators named Lucius Sergius Paullus, of Antioch, Pisidia, including one who was consul suffectus around AD 70, and another who was twice consul, Lucius Sergius Paullus, the father of Sergia Paulla, who married Quintus Anicius Faustus, Legate of Numidia in 198, and had Quintus Anicius Faustus Paulinus, governor of Moesia Inferior between 229 and 232
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Elymas
Elymas
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Elymas , also known as Bar-Jesus (Ancient Greek: Βαριεσοῦ, Aramaic: Bar-Shuma, Latin: Bariesu), is a Jew in the Acts of the Apostles, chapter 13,[1] in the New Testament. Acts of the Apostles calls him a magus, which the King James Bible here translates as "sorcerer". He is represented as opposing the disciple Paul the Apostle, who is called at this point for the first time with his Roman name, and Barnabas in the city of Paphos on Cyprus, when Sergius Paulus, the Roman Proconsul, wishes to hear Paul and Barnabas speak about Jesus. Because of this opposition, Paul claims that God had decided to make him temporarily blind. A cloud of darkness immediately begins blocking his sight;[2] after this Sergius Paulus is converted to Christianity .[3]
Elymas's intentions for Sergius
are unclear, only that he was desperate to keep him from receiving the
word about Jesus. Perhaps he had the proconsul's ear and was his advisor
on matters of faith. This would make sense as Sergius is obviously learned about Jewish teachings and Elymas is Jewish. The message Paul and Barnabas bring threatens the false-prophet's usefulness to the island's most powerful administrator.
Bar-Jesus received the same curse that Paul himself did: temporary blindness.[4]
It is clear from the passage that Bar-Jesus had the ear of the
proconsul and was well known throughout the region. He was a
self-proclaimed prophet of God[5] who may have had his own religious agenda.
Elymas stirred up a riot of Jews and pagans in Salamina (Salamis) against Barnabas, according to The Golden Legend.[6]
Name
Acts 13:8 says "Elymas the Magus (for so his name is translated) opposed them". "Elymas" is possibly derived from the Arabic ‘alīm "learned" or "wise", and may be used to translate magos.[7] Bar-Jesus means "Son of Joshua" or "Son of Jesus" in Aramaic.
2 Peter 3
The Day of the Lord
3 Dear friends, this is now the second letter I have written to you; in both letters, I want to develop a genuine understanding with a reminder, 2 so
that you can remember the words previously spoken by the holy prophets
and the command of our Lord and Savior given through your apostles. 3 First, be aware of this: Scoffers will come in the last days to scoff, living according to their own desires, 4 saying, “Where is the promise of His coming? Ever since the fathers fell asleep, all things continue as they have been since the beginning of creation.” 5 They willfully ignore this: Long ago the heavens and the earth were brought about from water and through water by the word of God. 6 Through these waters the world of that time perished when it was flooded. 7 But by the same word, the present heavens and earth are stored up for fire, being kept until the day of judgment and destruction of ungodly men.
8 Dear
friends, don’t let this one thing escape you: With the Lord one day is
like a thousand years, and a thousand years like one day. 9 The Lord does not delay His promise, as some understand delay, but is patient with you, not wanting any to perish but all to come to repentance.
10 But the Day of the Lord will come like a thief; on that day the heavens will pass away with a loud noise, the elements will burn and be dissolved, and the earth and the works on it will be disclosed. 11 Since
all these things are to be destroyed in this way, it is clear what sort
of people you should be in holy conduct and godliness 12 as you wait for and earnestly desire the coming of the day of God. The heavens will be on fire and be dissolved because of it, and the elements will melt with the heat. 13 But based on His promise, we wait for the new heavens and a new earth, where righteousness will dwell.
Conclusion
14 Therefore,
dear friends, while you wait for these things, make every effort to be
found at peace with Him without spot or blemish. 15 Also,
regard the patience of our Lord as an opportunity for salvation, just
as our dear brother Paul has written to you according to the wisdom
given to him. 16 He
speaks about these things in all his letters in which there are some
matters that are hard to understand. The untaught and unstable twist
them to their own destruction, as they also do with the rest of the Scriptures.
17 Therefore, dear friends, since you know this in advance, be on your guard, so that you are not led away by the error of lawless people and fall from your own stability. 18 But grow in the grace and knowledge of our Lord and Savior Jesus Christ. To Him be the glory both now and to the day of eternity. Amen.